More Information
Submitted: 09 March 2020 | Approved: 17 March 2020 | Published: 18 March 2020
How to cite this article: Rudrakshi C. Trends in Teledentistry. J Clin Adv Dent. 2020; 4: 004-005.
DOI: 10.29328/journal.jcad.1001014
Copyright License: © 2020 Rudrakshi C. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Trends in Teledentistry
Rudrakshi C*
Department of Periodontics, Krishnadevaraya College of Dental Sciences, Bangalore, India
*Address for Correspondence: Rudrakshi C, Department of Periodontics, Krishnadevaraya College of Dental Sciences, India, Fax; +91-080-28467084; Tel: 1. +91-9986110826; Email: [email protected]
Socioeconomic barriers appears to be the greatest threat to dental care apart from considering the geographic location of the population. Access to need of care becomes primary consideration and through teleconsultation it is possible to overcome these barriers. As oral cavity being gateway to entry of health problems, dental treatment becomes a pivotal in health care system. Tele medicine and Tele dentistry becomes effective in treatment of health problems, reducing the chances of late stage detection of the abnormalities. It allows us to utilize our time better and screen more patients. This article aims to provide amazing technology of Tele dentistry involving all the dental specialties to reach all the populations of the society.
Technology is all around us. Existence of life presently is in an electronic world where it is difficult to think of life without telephones, personal computers, electronic devices with internet network connectivity. According to the center for collected health policy states, Telehealth refers to a broad variety of technologies and tactics to deliver virtual medical, health, and education services. Tele medicine and Tele dentistry are technological innovations for health care to solve multitude of general and oral problems which can be beneficial to the aged and remote populations. These are exiting technologies having endless potential.
Teledentistry is the use of communication technologies like audio, video, data communication forward technologies to provides support dental care delivery, diagnosis, consultation, treatment, transfer of dental information and education linking them with the specialists in larger communities, reasonable cost global communications and colleagues instantly available. Teledentistry has found to be cost-effective alternative to a visual oral examination in Preschool children [1].
Teledentistry is a relatively new field that combines telecommunication technology and dental care. Tele dentistry event occurs depends on circumstances, such as all persons who must be involved are not able to be in the same physical location. Another determining facet is the judgment of the dentist or other oral health or general health practitioner, all acting in accordance with applicable state law, regulation or licensure [2]. Tele dentistry has its roots lies in telemedicine, which was first used by NASA in 1970s [3]. Skeletal framework of tele dentistry involves real time consultations and storage and forwarding, live video using audiovisual telecommunications technology, remote patient monitoring (RPM) and Mobile health (mHealth) using communication devices.
According to American Dental Association, 2 Synchronous tele dentistry (D9995) is delivery of patient care and education where there is live, two-way interaction between persons (e.g., patient; dental, medical or health caregiver) at one physical location, and an overseeing supervising or consulting dentist or dental provider at another location. The communication is real-time and continuous between all participants who are working together as a group. Use of audiovisual telecommunications technology means that all involved persons are able to see what is happening and talk about it in a natural manner. Asynchronous tele dentistry (D9996) is different as there is no real-time, live, continuous interaction with anyone who is not at the same physical location as the patient. Also known as store-and-forward, asynchronous tele dentistry involves transmission of recorded health information (e.g., radiographs, photographs, video, digital impressions and photomicrographs of patients) through a secure electronic communications system to another practitioner for use at a later time.
Access to care undeserved and undertreated population, co-effective early diagnosis, medical e- prescription, enhanced communication, aid to train dental personnel to conduct camps in remote areas, updating the dental knowledge with the newer technology through teledentistry. Even though initial setup is high maintenance is cost effective. It improves the dental hygiene of patient. Be more affordable than in office dentistry. Attends patient needs for modern forms of communication. Utilization of the telehealth services keep growing, can outreach millions of patients in coming years. Telecommunication via mobile health applications is especially beneficial to elderly people.
a) Teledentistry is a mode of dental service delivery that, when applicable, is reported in addition to the other procedures provided to the patient. b) Procedure delivery is by a natural person (e.g., dentist); the billing entity may be a natural person or a legal person (i.e., the facility where the service is delivered). c) The ADA’s “Comprehensive Policy Statement on Teledentistry” states that dentists and allied dental personnel who deliver services through teledentistry modalities must be licensed or credentialed in accordance with the laws of the state in which the patient receives service. The delivery of services via teledentistry must comply with the state’s scope of practice laws, regulations or rules.
Who has responsibility for services delivered via teledentistry? Responsibility, and liability, for services delivered is determined by applicable state law and regulations. Each dentist, hygienist and others involved in a teledentistry appointment should become familiar with applicable state or federal regulations to determine their liability exposure, and whether or not the person receiving care becomes their patient of record. Please note that “patient of record” may be defined differently under applicable state regulations. This could be a factor to consider in a teledentistry event where the patient and some members of the team of providers are in different states.
Technical problems may cause misdiagnosis/medical error. Literature of teledentistry practice largely depends upon the Qualitative assessment of studies of diagnostic accuracy (QUADAS) varied from high quality > 60% validity is varied with sensitivity (n = 8, 25-100%) specificity (n = 7, 68%-100%) Kappa statistics [4]. Studies with appropriate statistical levels to determine the validity of teledentistry exists.
It teaches general dentist when to refer a patient and how to treat more complicated cases, which can change the prospective of patients and practice style of a clinician and give them more choices in treating patients. Because of the advantages of teledentistry, teleconsultations are possible and valid.
Dental benefit plan reimbursements are, as today, payable to the billing entity on the claim submission, who may be a natural person (e.g., dentist) or a legal person (e.g., dental practice). Allocation of reimbursements is subject to the business relationships between the reimbursement’s recipient and other oral health or medical health practitioners involved in the tele dentistry event.
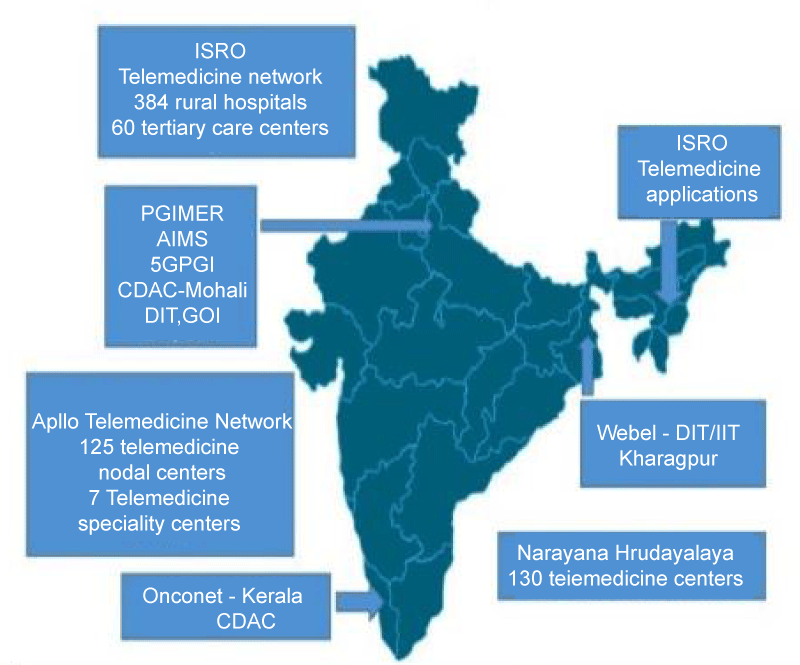
Figure 1: Telemedicine in India: Role of Government and private enterprises. Mathur P, Srivastava S, Lalchandani A, Mehta JL (2017). Evolving Role of Telemedicine in Health Care Delivery in India. Prim Health Care 7:260.
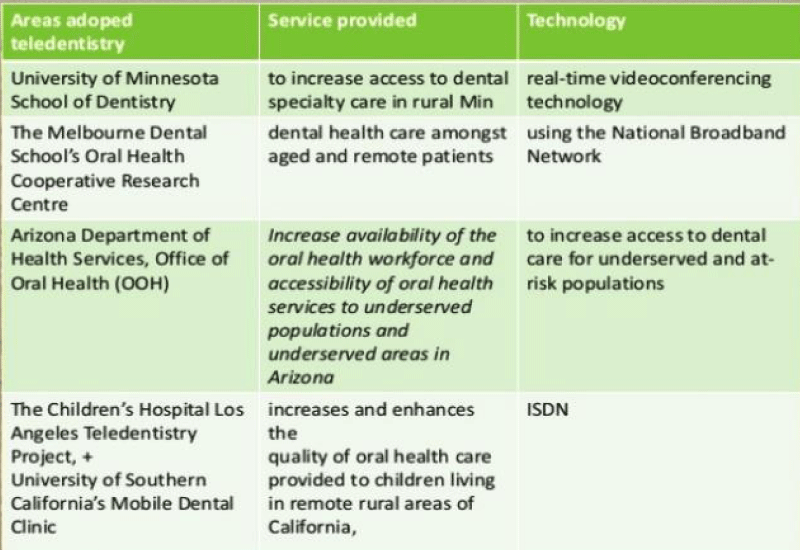
Figure 2: Tele dentistry across the world.
Tele dentistry are evolving to provide access of care to the inaccessible patients for early detection of diseases to ensure proactive and preventive care.
- Jampani ND, Nutalapati R, Dontula BS, Boyapati R. Applications of teledentistry: A literature review and update. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2011; 1: 37-34. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24478952
- D9995 and D9996 – ADA Guide to Understanding and Documenting Teledentistry Events Version 1 – July 17, 2017.
- Arora PC, Kaur J, Kaur J, Arora A. Teledentistry: An innovative tool for the underserved population. Digit Med. 2019; 5: 6-12.
- Alabdullah JH, Daniel SJ. Giant cell arteritis: A Systematic Review on the Validity of Teledentistry. 2018; 24: 639-648. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29303678